Fukushima reactors, after tsunami
On March 11, 2011, the Fukushima nuclear disaster shocked the world. Sadly, the thinkers in the anti-nuclear world were not complete surprised. We were startled, but we know that disasters, while unpredictable, are inevitable. Disasters are built into the nuclear power system. The best engineers are fallible. (Anyone who drives a car or uses a personal computer knows this.) We can engineer nuclear reactors to be “reasonably” safe – but that costs a lot of money. That’s why ALL nuclear reactors leak “acceptable” levels of tritium – it is too expensive to capture all the tritium.
We also know
- While the probability of an accident may be low, the probability is very high that an accident, if it occurs, will be
- In Three Mile Island, in 1979, Chernobyl, in 1968, and Fukushima, in 2011, we have four melt-downs and one partial melt-down since the Price Anderson Act was first signed into law in 1956. That’s four melt-downs in 56 years. While it’s a too small to give a precise statistical measure, it offers empirical data to suggest a high probability of a catastrophic accident every 14 years.
In command economies, such as existed in the Soviet Union, or exists in Iran and North Korea, it is illegal – and dangerous – to question the government. In market economies, such as exist in the United States, Europe, and Japan, there are strong incentives to cut corners.
But back to Fukushima – following the disaster, nearly all of Japan’s 54 Nuclear Plants have been shut down due to pressure by the Japanese people.
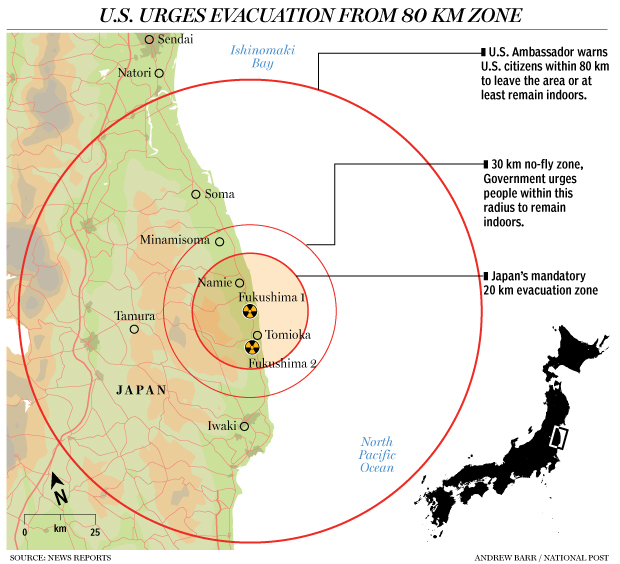
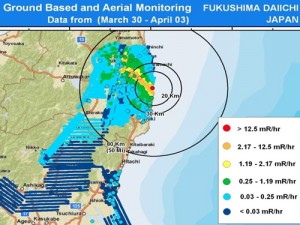
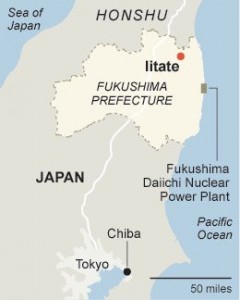
The disaster deposited radioactive fallout on a semicircular area of Japan with a radius of 50 miles. It caused the permanent displacement of 160,000 people. An unknown amount of radioactive materials have been flushed into the Pacific Ocean. TEPCO, the owners of the reactors, have a $100 Billion liability (that will probably be absorbed by Japanese citizens over the next 20 or 50 years).
So after Fukushima, the question that we ought to be asking is not: “Can solar, wind, geothermal, marine current and other sustainable technologies meet our energy needs?”
The question is: “HOW can solar, wind, geothermal, marine current and other sustainable technologies meet our energy needs?”
I will be speaking on Monday, March 5th, at 6:00pm, at the Unitarian Universalist Meeting House on West Front Street in Lincroft, NJ. This will be part of a series of discussions along a 250 mile walk from Oyster Creek, in Ocean County, NJ to Vermont, Yankee, in Vernon, Vermont. I will make a statement similar to the talk at the Space Coast Green Living Festival, reported here.
A group of Japanese Buddhists, Fukushima eye-witnesses and US citizens will be walking over 250 miles from Oyster Creek to Indian Point to the Vermont Yankee Nuclear Power Plants to bring awareness of the terrible risks of nuclear power. The “No More Fukushimas Peace Walk” is being led by Jun Yasuda.
Scheduled events open to the public:
Friday March 2nd, 7pm, “Implications of the Fukushima Nuclear Disaster for the U.S and continuing Japanese crisis”
Little Theatre, Georgian Court University, 900 Lakewood Ave, Lakewood N.J.
Speakers:
- Sachiko Komagata, P.T., Ph.D, and Associate Professor & Chair, Department of Holistic Health & Exercise Science
- Rachel Dawn Fudim-Davis, New Jersey Organizer, Food & Water Watch
- Jeff Tittel, Director of Sierra Club, NJ Chapter
- Sister Mary-Paula Cancienne, RSM, PhD.
Hosts: Sister Mary Bilderback, Mary Paula Cancienne
For information Kasturi DasGupta, PhD 732-987-2336
Saturday, March 3, 6:00 pm,
Sky Walk Cafeteria, 2nd Floor, 129 Hooper Ave, Toms River, NJ (Connected to parking garage)
Speakers:
- Sky Sims, Sustainable energy specialist;
- Joseph Mangano, Executive Director of Radiation and Public Health Project;
- Ed M. Koziarski and Junko Kajino, Filmakers
For information Burt Gbur, 732-240-5107
Sunday, March 4th, 6:00 pm,
Murray Grove Retreat Conference Center, Lanoka-Harbor, NJ Church Lane and US Highway 9
Speakers:
- Willie DeCamp, Save Barnegat Bay,
- Greg Auriemma, Esq., Chair, Ocean County Sierra Club,
- Peter Weeks.
For information Matt Reid, 609-312-6798
Monday, March 5th, 6:00pm,
Unitarian Universalist Meeting House, West Front Street, Lincroft, NJ
Speakers:
- Larry Furman, “Beyond Fuel: The Transition from Fossil Fuel and Nuclear Power to Sustainable Energy.”
- Japanese walkers share their post-Fukushima experiences in Japan
For Information:. Elaine Held (732-774-3492).
Thursday, March 8, 6:00 pm
Puffin Foundation, 20 Puffin Way, Teaneck, N.J.
Speaker:
- Sidney Goodman, Author ‘Asleep At the Geiger Counter: Nuclear Destruction of the Planet and How to Stop It’, ISBN: 978-1-57733-107-0, available from Blue Dolphin Publishing, and elsewhere.
For information Jules Orkin, 201-566-8403
The walk will start at 10am on Saturday, March 3rd near the Oyster Creek area, and end at 129 Hooper Ave, Toms River. Starting times and places for March 4th and 5thwill also be announced on February 27th.
————————————————–
The mission of the Walk:
A plea for the people of New Jersey, New York and New England to recognize the grave dangers that nuclear energy poses to our lives, property, and all life on the planet.
We walk together in love and solidarity for a nuclear free future, and a more just, sustainable, and compassionate world built on respect for all living beings.
JOIN THE WALK FOR AN HOUR OR A DAY.
Edith Gbur 732-240-5107
Christian Collins 413-320- 2856
Cathy Sims 732-280-2244