![]() Tweet “The United States,” according to Robert Barro, who teaches economics at Harvard and is a “fellow” at the Hoover Institution, “is in the third year of a grand experiment by the Obama administration.” This is inaccurate. Obama is the President, but the US Constitution provides a framework in which power is divided into three branches of the Federal government, and the power of the each of the branches is checked and balanced by the others, and “all power not expressly granted to the federal government is held by the states and the citizens. It would be more accurate to say that the United States is in the third year of a grand experiment by the Obama administration, the Congress, the Judiciary, the Republican Party, various special interests, and the citizens.
Tweet “The United States,” according to Robert Barro, who teaches economics at Harvard and is a “fellow” at the Hoover Institution, “is in the third year of a grand experiment by the Obama administration.” This is inaccurate. Obama is the President, but the US Constitution provides a framework in which power is divided into three branches of the Federal government, and the power of the each of the branches is checked and balanced by the others, and “all power not expressly granted to the federal government is held by the states and the citizens. It would be more accurate to say that the United States is in the third year of a grand experiment by the Obama administration, the Congress, the Judiciary, the Republican Party, various special interests, and the citizens.
Barro published this flawed analysis in “How to Really Save the Economy, “an op-ed in the New York Times, published Sept. 10, 2011.
“How is the experiment going?” Barro asks rhetorically. “Not well,” he answers.
How could it? On January 16, 2009, a week before the Inauguration, Rush Limbaugh, one of the leaders of the right wing of the United States said, “I hope Obama fails.” (The text is on Limbaugh’s site. An audio is on You Tube.) As I wrote, on Popular Logistics, here, a hope that the President fails is hope that the United States fails.
As was reported, here, in the Washington Post on August 6, 2011, and here on Popular Logistics, on August 8, 2011, John Boehner, Eric Cantor, Paul Ryan, and the “Young Guns,” their Republican comrades in the House of Representatives, PLANNED as far back as January, 2009 to use the debt ceiling to create a political crisis. The Republicans have been trying to actualize Mr. Limbaugh’s hopes.
Barro is a professor of neoclassical economics, and a fellow of the Hoover Institution. What he doesn’t understand, and what President Herbert Hoover didn’t understand, is that under economic conditions such as we see today, while businesses and government are able to create jobs, business owners are risk averse, and won’t risk capital. The government MUST create jobs, because businesses won’t. Everyone who has a job and a 10 year old car, and is hesitant with regards to buying a new car, understands this. John Maynard Keynes understood this. Franklin Delano Roosevelt understood this. Herbert Hoover didn’t – which is why he lost to Mr. Roosevelt in 1932, and why, 36 years later, President Nixon said “We are all Keynesians now.” (Note that Mr. Nixon has been called many things. However, “Liberal” is not one of them.)
So how do we really save the economy? See Part Deux.
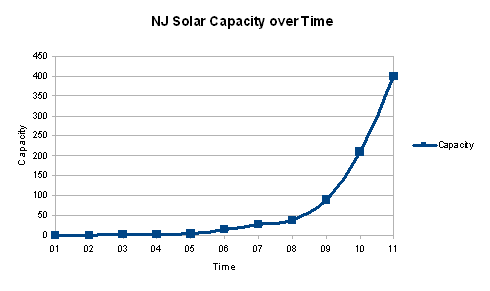
One of the best kept secrets in New York City is the existence of a 40 kilowatt (KW) photovoltaic solar array on the Whitehall Street terminal of the Staten Island Ferry, pictured above, and first covered in Popular Logistics in 2007, here.
There are 90,000 public schools in the United States. Suppose we were to install a 40 KW solar energy system on each of them. PV solar modules require very little maintenance over their 35 to 45 year life expectancy. At a cost of $5,000 per kilowatt of nameplate capacity, each of these 90,000 systems would cost $200,000. This 3.6 gigawatts of distributed daylight-only capacity would cost about $14.4 billion. The total costs would probably be less because PV Solar is subject to economic forces like Moore’s Law.
It seems to make sense to use taxpayer monies to finance these systems; taxpayer monies pay the electric bills for public schools and other public infrastructure.
Every public school in the country would have a power plant that generates power, during the day, with no fuel cost and no waste. And with no associated mining, processing, transportation, fuel costs and no waste management costs. At $5.00 per watt, or $5 billion per gigawatt, the capital costs are lower than the costs of new nuclear and significantly lower than the costs of coal with carbon sequestration, with none of the risks or hazards associated with the systems: no arsenic, mercury, lead, thorium, uranium, zinc, or carbon.
But what are the other implications? What would it give us? Again. see Part Deux