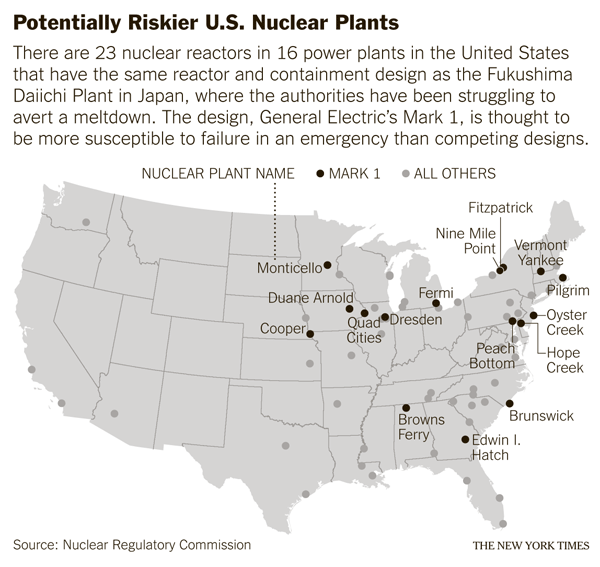
before the catastrophe
(Second in a series on the ecological economics, financial ramifications, logistics, and systems dynamics of nuclear power in the light of the ongoing catastrophe at Fukushima.)
Cary Krosinsky, VP at Trucost, is once again teaching a course on Sustainable Investing at the Center for Environmental Research and Conservation, CERC, at Columbia University. At the March 10 seminar a student spoke about her recent 400% “home run” in a uranium mining operation. She bought in because the earnings were high, debt was low, yet the price was low. It was a classic “value” play of a well-run company undervalued by the market.
But would a “Sustainable Investor” buy a uranium stock? My goal, as a “Sustainable Investor” is “To outperform the S&P 500 index by investing in the top companies, from the perspective of environmental impact, sustainability, management and governance, in the sectors I hope will thrive over the next 25 to 50 years.”

After Tsunami, STR/AFP/Getty Images
Cary didn’t exactly write the book on sustainable investing. He edited it. In Sustainable Investing, the Art of Long Term Performance, copyright, (C) Cary Krosinsky and Nick Robins, 2008 (Earth Scan) he defines “Sustainable Investing” as “an approach to investing driven by the long-term economic, environmental, and social risks and opportunities facing the global economy.”
Jane and Michael Hoffman, in Green, Your Place in the New Energy Revolution, wrote that the nuclear industry was killed not by the protesters at Seabrook, and the environmentalists at Environmental Defense (EDF), Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS), or local groups like NY Public Interest Research Group (NYPIRG) who hired lawyers and scientists to force the utilities to build plants more safely. But it was bankers on Wall Street who, in the aftermath of Three Mile Island and Chernobyl, realized that their Million-dollar investments could turn into Billion-Dollar liabilities in seconds, and stopped investing in new nuclear power plants. Even though their liability was limited by the Price Anderson Act in the US and by corresponding legislation in other governments, they might never see a return on their investment. Despite promises by Presidents George W. Bush and Barack Obama of loan guarantees – government subsidies – to build plants, Wall Street is reacting to Fukushima with a mix of caution and skepticism. According to the Wall Street Journal, “The Street” is now, once again, bearish on nuclear power but it is looking again at solar and wind. (click here).
“The nuclear industry is on edge after last week’s quake caused serious damage to several reactors. Bank of America Merrill Lynch cut its stock-investment rating of Entergy ($69.76, -$3.93, -5.33%) and Scana Corp. (SCG, $38.54, -$1.51, -3.77%) to underperform from neutral, citing risks including delays and higher approval costs for relicencing of existing plants. Dahlman Rose says as many as 10 reactors could be affected, which consume the equivalent of 340,000 pounds of uranium each month. The firm cut its price targets for Cameco Corp. (CCJ, $30.90, -$6.48, -17.34%) and Uranerz Energy Corp. (URZ, $3.08, -$0.87, -22.03%).
“Renewable-energy stocks rose in the U.S. in the wake of the nuclear-plant concerns in Japan putting a fresh pall over that industry and some investors believing non-nuclear energy sources away from fossil fuels will get a boost. Solar companies are leading the way, including First Solar Inc.
“CreditSights and other analysts form a chorus that the “nuclear renaissance” of new plants in emerging markets and developed nations will slow, while the potential for new design and safety measures could challenge sector economics .
“Japan’s nuclear crisis is hammering shares in the U.S. nuclear sector, but investors should keep an eye on engineering-and-construction stocks that work in the sector as well, JP Morgan says, citing Shaw Group Inc. Babcock & Wilcox Co. , URS Corp. and EnergySolutions Inc. “We believe the safety features of newer generation reactors will be considerably more advanced” than the older Fukushima units causing havoc over the weekend, the firm writes, but still sees likelihood that renewed nuclear worries are a headwind for these stocks.”
Here are the data:
| Company |
Symbol |
Quote |
Change |
Percent |
| Entergy |
ETR |
$69.76 |
($3.93) |
-5.33% |
| Uranium Energy |
UEC |
$4.03 |
($0.82) |
-16.91% |
|
|
|
|
|
| Shaw |
SHAW |
$30.92 |
($7.49) |
-19.50% |
| Babcox |
BWC |
$31.58 |
($2.79) |
-8.12% |
| URS |
URS |
$43.88 |
($1.58) |
-3.48% |
|
|
|
|
|
| First Solar |
FSLR |
$145.13 |
$5.39 |
3.86% |
| (data from March 14, 2011.) |
|
|
|
My analysis –
Peter Crowell, professor of Finance and Logistics in the Marlboro College MBA in Managing for Sustainability asked “What happens if you – we – take away all the subsidies?”
If we take away the subsidies from nuclear power, the industry would collapse. The same holds for the fossil fuel industry – if you factor in the hidden “externalized” costs of environmental cleanup. It makes no sense to build nuclear plants, or coal plants, drill for oil or use fracking for natural gas. These are more expensive to build, run, and maintain than solar and wind. Rather than keeping nuclear and fossil fuels on life support while fuel gets harder and more expensive to extract we need to put our best engineering minds to work on clean, sustainable power.
And I expect the vultures on Wall Street to buy Japanese stocks as soon as they sense the market has hit bottom, but only if they see investment in infrastructure.
Index to the series
- Earthquake, Tsunami and Energy Policy, March 11-13, 2011. Here.
- After Fukushima, Wall Street Bearish on Nuclear Power. March 14, 2011. Here.
- Fukushima: Worse than Chernobyl? Here.