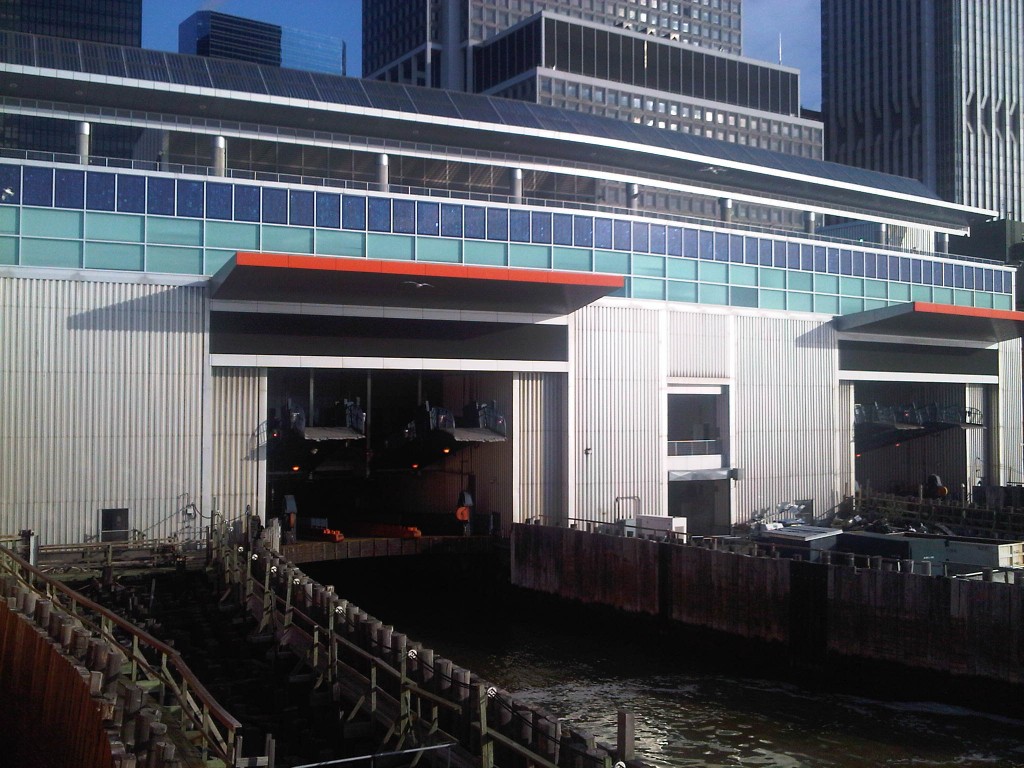
40 KW PV Solar Array on SI Ferry Terminal
While Chinese subsidies of their solar energy industry have decimated the manufacturing base of the American solar industry, solar energy continues to expand across the country.
What if we stimulated the solar industry with a public works program?
What if we decided to deploy a 40 kilowatt photovoltaic solar array on each of the approximately 90,000 public schools in the country?
The best kept secret in NYC may be found on the Staten Island Ferry, or more precisely, on the south roof of the Whitehall Street terminal. It’s a 40 kilowatt photovoltaic solar array.
Taxpayers pay the electric bills of the ferry terminal, which today are much lower because of the energy the system produces. Taxpayers also pay the electric bills of public schools, courts and other municipal, state and federal office buildings – and the externalized costs of pollution and “health effects” related to mining coal and uranium, drilling oil or frakking gas.
I met Senator John Kerry at the Harvey Nash Inc. Leadership Breakfast at the Plaza Hotel in NYC on Friday, March 2, 2012. At the conclusion I asked him to consider a 40 kw photovoltaic solar energy system on each of the approximately 90,000 public schools in the US.
At $5.00 per watt, which is less than the cost of new nuclear and much less than coal with carbon sequestration, these 90,000 systems would cost $18 billion. They would produce electricity without burning fuel, creating wastes, or creating targets for terrorists, and would pay for themselves in eight to 15 years, depending on the market price of electricity. They would also produce energy for 25 to 40 years – paying for themselves several times over.
This kind of a public works project would create jobs. Even if we didn’t mandate that these used products made in American factories, which I think we should, installation and maintenance would have to be local.
It would also lessen our dependence on fossil fuels.
And each solar energy powered building could be designed to generate electricity during the day during an emergency which shuts down the grid, further enhancing our emergency response capability.
Senator Kerry responded that this would be a perfect project for the Infrastructure Bank that he wants to create. However, the political climate is such that it can’t get done.