 At a seminar on June 9, 2011, on securing the mobile worker, Apple‘s representative said “We truly did not understand what we built.” That’s a direct quote. He went on to say “Here’s how they use it at GE, and Hyatt, and in the pharmaceutical industry.” A few minutes later he said “When users tell us what they can’t do, what they need to do, we listen, so tell us what you need.” At seminars on Microsoft‘s products, their consultants describe their software by saying “This is what we built, this is what it does, and here are our best practices – this is how you should use our software.”
At a seminar on June 9, 2011, on securing the mobile worker, Apple‘s representative said “We truly did not understand what we built.” That’s a direct quote. He went on to say “Here’s how they use it at GE, and Hyatt, and in the pharmaceutical industry.” A few minutes later he said “When users tell us what they can’t do, what they need to do, we listen, so tell us what you need.” At seminars on Microsoft‘s products, their consultants describe their software by saying “This is what we built, this is what it does, and here are our best practices – this is how you should use our software.”
This is it. Apple’s “We truly did not understand what we built,” versus Microsoft’s “This is what we built, this is what it does, and here are our best practices – this is how you should use our software.” These statements define the corporate cultures.
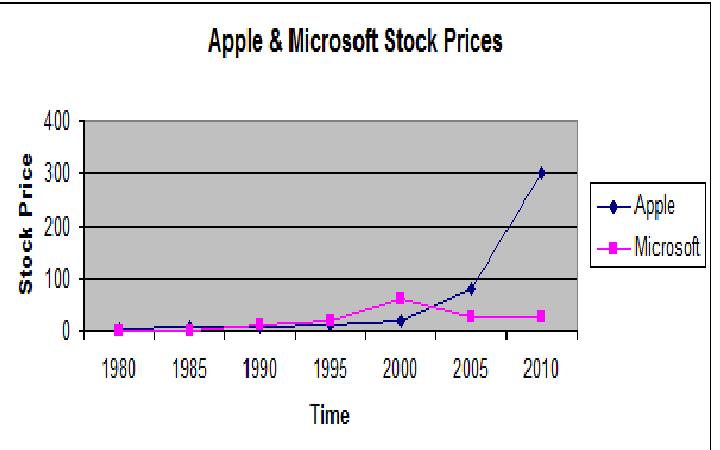
Apple, at $325 per share, is a $300 billion company. With earnings of 21 per share, it has a price earnings ratio of 15.8. It has no debt. It is down slightly from it’s high of around $350 per share, reached a few weeks ago. There are 46,000 employees. Net income of 5.99 Billion on $24.67 Billion. Microsoft, at $24 per share, is a $200 billion company. With earnings of $2.92 per share it has a P/E of 9.44. There are 89,000 employees, $16.4 billion revenue and $5.2 billion net income.
Microsoft’s income per dollar of revenue is higher – but they don’t make hardware. Revenue per employee at Microsoft is $184,000. Revenue per Employee at Apple is $536,000. Income per Employee at Microsoft is $58,000. Income per Employee at Apple is $130,000.
These data are summarized below,
| Employees | Net Income | Revenues | Inc / Emp | Rev / Emp | |
| (Millions) | (Millions) | ||||
| Apple | 46,000 | $5,990 | $24,670 | $130,217 | $536,304 |
| Microsoft | 89,000 | $5,200 | $16,400 | $58,427 | $184,270 |
When I last looked at Apple and Microsoft, October 30, 2010, here, Apple was 305.24 per share, with an EPS, of $15.15 and a P/E of 20.147. It’s market capitalization was $279.59 Billion. Microsoft was $26.28, with an EPS of 2.11, P/E ratio of 12.48 and market capitalization of $227.42 Billion, $52 Billion less than that of Apple. Today Apple’s market capitalization is up 25% to $300 billion and Microsoft’s market capitalization is down about 12% to $200 billion. Apple’s market capitalization is $100 billion higher than Microsoft’s. Apple’s all time high stock price was a few weeks ago, and I expect it will bounce back and keep climbing as long as they keep selling hardware and software that shifts the paradigm. Microsoft’s was in 1999. I don’t expect Microsoft to go out of business, but it’s days of shifting the paradigm and tremendous growth are gone.
 The iPad (Apple site, here) is a paradigm shifting device. It has a dual core A5 processor, 16, 32, or 64 GB of flash memory, and no moving parts (other than electrons, which are hard to keep still). Treated properly, it should last for 10 or 20 years. It adds a layer of durability and obsolescence resistance to personal electronics. It puts us on the road from “disposable” consumer electronics back to durable, sustainable consumer electronics (click here).
The iPad (Apple site, here) is a paradigm shifting device. It has a dual core A5 processor, 16, 32, or 64 GB of flash memory, and no moving parts (other than electrons, which are hard to keep still). Treated properly, it should last for 10 or 20 years. It adds a layer of durability and obsolescence resistance to personal electronics. It puts us on the road from “disposable” consumer electronics back to durable, sustainable consumer electronics (click here).
And it’s selling by the millions. Apple has sold 200 million iOS devices – iPhones, iPads, iPods Touch, that’s one for two out of three Americans. It’s sold 25 Million iPads, 14 million in 2010 and 11 million in the first half of 2011. The sales projections from Wall Street are tremendous, (Florin at UnWired, Schonfeld at Tech Crunch, Elmer-DeWitt at Fortune). People buy multiple devices, e.g., iPhone and iPad or iPod Touch and iPad. These are driving sales of music, apps – by the billions – and the Mac. Microsoft is buying SKYPE, which is a great company with a great product but it doesn’t know how to make money. Apple is going up, both in terms of market capitalization and earnings. Microsoft is going nowhere.


