On May 25, 1961 President John Kennedy said, “I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him safely to the earth.” (Kennedy library and NASA)
On May 25, 1961 President John Kennedy said, “I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him safely to the earth.” (Kennedy library and NASA)
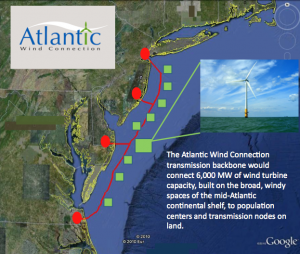
Ten years ago, before Sept. 11, Jim Gordon and his team set out to build a small wind farm on the waters on which the young President, his wife, brothers, sisters, nieces and nephews sailed. Size is relative. It’s small compared to a large coal or nuclear power complex. The wind farm will be composed of 130 turbines and produce up to 430 megawatts of power (here).
 In 2010 Jim Gordon and Cape Wind, LLC, finally, got their permits to build the wind farm. For a variety of reasons it took longer for Cape Wind, LLC to get the permits to build the wind farm than it took this nation to land a man on the moon and bring him home safely. Had the wind farm been built by the winter of 2004, Cape Wind would have provided power during the bitter January of ’04, the heat wave of ’05, and every day, especially the coldest days of winter and the hottest days of summer – when the winds are strongest and New Englander’s electricity needs are highest.
In 2010 Jim Gordon and Cape Wind, LLC, finally, got their permits to build the wind farm. For a variety of reasons it took longer for Cape Wind, LLC to get the permits to build the wind farm than it took this nation to land a man on the moon and bring him home safely. Had the wind farm been built by the winter of 2004, Cape Wind would have provided power during the bitter January of ’04, the heat wave of ’05, and every day, especially the coldest days of winter and the hottest days of summer – when the winds are strongest and New Englander’s electricity needs are highest.




It’s also clear, from reading Cape Wind, by Wendy Williams and Robert Whitcomb, that the alliance to “Save Our Sound,” created an anti-wind rogue’s gallery, a bipartisan coalition of moneyed special interests which led Senator Edward M. Kennedy, D-MA, Governor Willard Mitt Romney, R-MA, Senator Ted Stevens, R-AK, Representative Dan Young, R-AK, Sen. Trent Lott, R-MS, Sen. John Warner, R-VA, and very wealthy residents of Cape Cod, including Bill Koch, the late Richard Egan, Rachel “Bunny” Lambert Mellon (Sen. Warner’s ex-mother-in-law), professional environmentalist Robert F Kennedy, Jr. to obstruct the regulatory and the legislative processes and which slowed the development of Cape Wind and offshore wind farms off of the mid-Atlantic and elsewhere.
For them to oppose this project or say “I favor wind power, as long as it’s somewhere else,” was and remains cynical. Given that we have combat troops in Iraq, Afghanistan, and Libya, that Alan Greenspan, Chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1987 to 2006 described the mission in Iraq as a war for oil, was unpatriotic, perhaps traitorous.

 Yet another bipartisan coalition rose up to challenge them and support Cape Wind: Ted Roosevelt, IV, who lives on the Cape, Rep. Jim Bass, R-NH, Sen. Olympia Snowe, R-ME, Sen. John McCain, R-AZ, Sen. Jeff Bingaman, D-NM, Sen. Pete Domenici, R-NM, Matt Patrick, Massachusetts, Gov. Deval Patrick, Greenpeace, unions, Fox News’ Sean Hannity. What these politicians have in common is an understanding of the values of energy independence and renewable energy.
Yet another bipartisan coalition rose up to challenge them and support Cape Wind: Ted Roosevelt, IV, who lives on the Cape, Rep. Jim Bass, R-NH, Sen. Olympia Snowe, R-ME, Sen. John McCain, R-AZ, Sen. Jeff Bingaman, D-NM, Sen. Pete Domenici, R-NM, Matt Patrick, Massachusetts, Gov. Deval Patrick, Greenpeace, unions, Fox News’ Sean Hannity. What these politicians have in common is an understanding of the values of energy independence and renewable energy.
Popular Logistics is a policy blog, not a politics blog. However, it’s worth noting that several political campaigns were won in Massachusetts by Democrats who supported Cape Wind, including Matt Patrick, the 5-term Democratic Representative of the 3rd District of Barnstable, Cape Cod, and Deval Patrick who started his 2006 Gubenatorial campaign in front of the Hull, MA, wind turbine.
Mitt Romney, who signed Ted Kennedy’s health care plan into law in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, (also known as Obamacare 1.0) appears to be running for President in 2012. He lost in the 2008 Primary to John McCain. Mr. Romney signed on to the Kennedy-Koch-Egan-Mellon anti-Cape Wind jihad. Americans favor wind power. Will they support Romney in 2012?
Scott “Mitt-Lite” Brown, said (here) “While I support the concept of wind power as an alternative source of energy, Nantucket Sound is a national treasure.” Massachusetts voters favor Cape Wind 70 to 30. Will they support Brown in his re-election campaign in 2012? The Statue of Liberty is a “National Treasure,” as is the Constitution. I last visited Cape Cod when I was 7. Nantucket Sound is not a “National Treasure.” Getting America off coal, oil, natural gas, and nuclear power, moving to clean, renewable, sustainable energy means our children and grandchildren will enjoy our national treasures.
In their book Williams and Whitcomb suggest that Senator Kennedy may have realized that he had made a bad decision in opposing Cape Wind, but that for a variety of reasons he refused to back down. They may be right. While I think Kennedy was wrong, I can’t speak to whether he came to that understanding. As I noted on this blog, back in August, 2009, (here) President Obama said of Ted Kennedy,”His ideas and ideals are stamped on scores of laws and reflected in millions of lives: in seniors who know new dignity; in families who know new opportunity; in children who know education’s promise; and in all who can pursue their dream in an America that is more equal and more just, including myself.”
Obama said “More equal and more just,” but he didn’t say “perfect.” America is not perfect. It is nation of men and women governed by the rule of law. The laws are not perfect, and neither are the men and women who make, enforce and interpret the laws.
Our energy policy is electricity flows when people flip a switch. Most of that electricity comes from burning fossil fuels and harnessing nuclear fission. We can pretend that the carbon we are pumping into the oceans and the atmosphere will have no effect, that we have unlimited supplies of fossil fuels, and uranium, that all the waste from coal mining, processing, transporting, and burning, and all the radiation leaks from nuclear plants (and radioactive waste from coal) are trivial or routine. Or we can get real. The choice is between coal, oil, methane, and nuclear, or wind, solar, tidal, and geothermal. I choose wind, solar, tidal and geothermal; for myself, for my backyard, not just for people who are my equal in the eyes of the law, whether they have more or less money than me.

—
Index to the series that explores Offshore Wind and Politics:
- Cape Wind, Leadership and Vision, here.
- Why Cape Wind Still Matters, here.
- Ted Roosevelt, IV, on Cape Wind (coming soon).