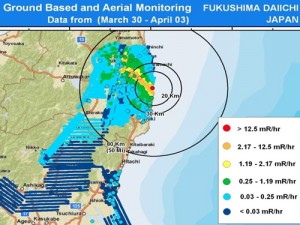
I drew four conclusions after reading Hiroko Tabuchi’s article, A Confused Nuclear Cleanup, in the NY Times, and looking at the US Government’s evacuation map, pictured above (obtained at the National Post, here.
- The Fukushima disaster is bad, really bad.
- The Japanese want to clean it up; but don’t know how.
- The nuclear industry in the USA is just like the nuclear industry in Japan – and that’s also really bad.
- In a market economy there may to too much pressure to increase shareholder value to spend enough on safety. (In a command economy, such as existed in the Soviet Union and exists in China, North Korea, and perhaps, Iran, it is illegal to criticize the government and therefore likely that necessary investments in safety will not be made.)
Here are the essential facts, as reported:
The Japanese government wants to clean an 8,000 sq mi area near Fukushima [about the size of New Jersey] to allow residents to return to their homes.
A day laborer wiping down windows at an abandoned school nearby shrugged at the work crew’s haphazard approach. “We are all amateurs,” he said. “Nobody really knows how to clean up radiation.”
The Japanese government awarded the first contracts to three giant construction companies — corporations that have no more expertise in radiation cleanup than anyone else does, but that profited hugely from Japan’s previous embrace of nuclear power.
“We are building expertise as we work,” said Fumiyasu Hirai, a Taisei spokesman. [Taisei is one of the three companies.] “It is a process of trial and error, but we are well-equipped for the job.”
“It’s a scam,” said Kiyoshi Sakurai, a critic of the nuclear industry and a former researcher at a forerunner to the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, which is overseeing this phase of decontamination. “Decontamination is becoming big business.”
The cleanup contracts, Mr. Sakurai and other critics contend, are emblematic of the too-cozy ties they say have long existed between the nuclear industry and government.
“The Japanese nuclear industry is run so that the more you fail, the more money you receive,” Mr. Sakurai said.
Though big companies have won the main contracts so far, the actual cleanup — essentially a simple but tedious task of scrubbing and digging — is being carried out by numerous subcontractors and sub-subcontractors, who in turn rely on untrained casual laborers to do the dirtiest decontamination work.
This tiered structure, in which fees are siphoned off and wages dwindle each step down the ladder, follows the familiar pattern of Japan’s nuclear and construction industries.
Fukushima coverage on Popular Logistics:
- Earthquake, Tsunami, and Energy Policy, March 11, 2011
- Nuclear Power: What Future?, March 27, 2011,
- Nuclear Power and Russian Roulette, June 20, 2011
- “Three Meltdowns at Fukushima” – Washington Post, July 11, 2011,