An Iceberg
First conclusion of a series that began after Earth Day and includes Fossil Fuels and a Walk on the Moon, Drill Baby Drill or Drill Baby Oops, Magnitude, Part 1, One Month After, The Chernobyl of Fossil Fuel?, and Magnitude, Part 2. )
As I wrote on Earth Day, “In 100 years our descendants will not be burning coal, oil, natural gas or using nuclear fission. They might be using terrestrial nuclear fusion. They will be using solar, wind, geothermal, marine current hydro, tidal energy systems – clean, renewable, sustainable energy systems. No fuel: No Waste. No mines, mills, wells, spills. No arsenic, lead, mercury, selenium, thorium – no carbon or fly ash to be contained, sequestered, or to leak.
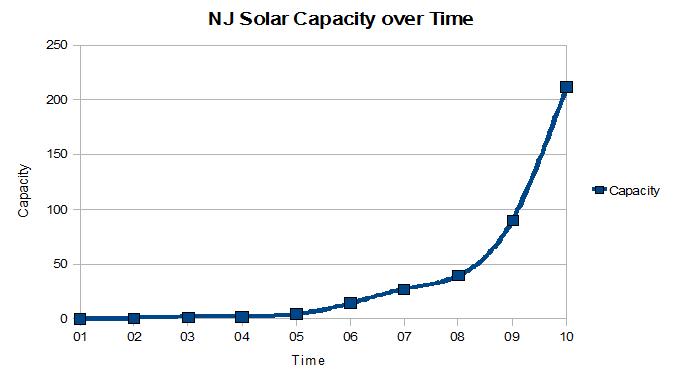
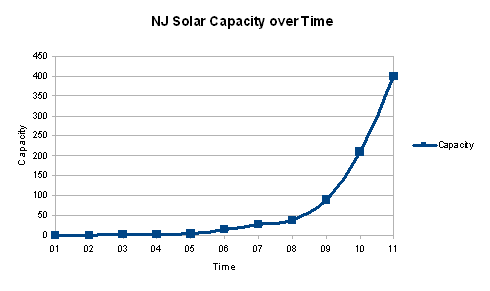
“We have started. California and New Jersey lead the U. S. Germany and Spain lead Europe. Boeing and Richard Branson’s Virgin Atlantic want to build aircraft that run on biodiesel. We need to move forward in a big way – to 100% clean energy in 10 years, to retrain coal miners and oil rig operators to build and run solar arrays and wind turbines, and dig deep geothermal systems.”
Otherwise the Deepwater Horizon Explosion at the Macondo oil field, the oil spills in Ecuador and Nigeria, the coal ash floods like the TVA Kingston Steam Plant, coal mine disasters like at Upper Big Branch, spills like the Exxon Valdez, and events like Three Mile Island and Chernobyl will be ‘”Business as Usual.”
A friend of mine who works for BP, and who would like to work for BP Solar, tells me that most BP staff don’t go to work thinking “How can I destroy the earth today.“ They are, she says “focused on obtaining and selling oil.” Few consider themselves environmentalists. Many see this as business as usual. “Oil spills happen,” they say. They are “focused on getting petrochemicals to market.”
The Macondo oil field that was tapped by the Deepwater Horizon could have contained 1 Billion Barrels of crude. It could have been one of the largest oil discoveries in the world .” (Click here for CBS and here for Times of London). The well could gush oil for YEARS and could have met US needs in 2007 – 21 Million Barrels per Day – for 47 days (here).
This volume of crude oil – 1 Billion Barrels – could explain the explosion. The equipment was built to operate at 20,000 PSI and withstand 60,000 PSI. It the pressures exceeded the limits, then the equipment could have failed. Simple. And Catastrophic. When you consider the pressures under 5000 feet of ocean, and the pressure of 1 Billion Barrels of oil, when you have engineers scratching their head saying “I don’t know, I never saw anything like this. What do You think we should do?” One the thing to do is run like hell.

An Orca
As was noted earlier in the series, like the iceberg pictured above and the Orca pictured at left, this is a singularity. But it has precedents.
- TVA Kingston: 1.2 Billion Gallons of toxic coal ash sludge, upstream of Kingston, Tennessee, 12/22/08.
- Chevron Texaco: (alleged) 18 Billion Gallons (428.6 million barrels) of Oil Process Waste, Rainforests of Ecuador, 1964 to 1990.
- Oil Fires of Kuwait: 6 Million Barrels per Day, up to 6 Months, 1991.
- Exxon Valdez: 250,000 Barrels, Prince William Sound, 1989.
- The Niger Delta, in Nigeria, 250,000 Barrels per year for the last 50 years (click here), “Big oil spills are no longer news in this vast, tropical land….has endured the equivalent of the Exxon Valdez spill every year for 50 years by some estimates…. Perhaps no place on earth has been as battered by oil, “

Flares in the Jungle
The TVA coal ash flood (here, here, here), the Upper Big Branch Mine accident (here, here), and the Deepwater Horizon at Macondo may be the “Trifecta” of American Fossil Fuel Disasters. But, like the problems in Ecuador (here) and Nigeria (here), these are “Systems Problems” – built into the system. The only way to eliminate them is to change the system.
This is what precisely what some people are trying to do. Students and faculty in the Marlboro MBA in Managing for Sustainability at the Marlboro College Graduate Center in Brattleboro, Vermont. They think about “Changing the Climate of Business.” And they may be are on to something, as are like minded people at the Presidio, the Fowler Center for Sustainable Value, at Case Western, and Columbia University’s Earth Institute.
Here’s an idea that will enable BP to make things right, change their image, and even make money. Suppose BP Solar built new factories in Florida and Louisiana, and hire former petrochemical and seafood workers – and churned out 25,000 to 50,000 PhotoVoltaic solar modules and 1,250 to 2,500 inverters per day. This would be 5 to 10 megawatts per day, 160 to 300 mw per month, 600 mw to 1.2 gigawatts per year.
According to my back of the envelope calculations, we need about 50 gw of solar in this country, along with 200 gw of wind, and 50 to 100 gw of other CRS (Clean, Renewable, Sustainable) generating capacity, so this is a drop in the bucket. But this is real change. It’s defining moment, substantive, shake the cobwebs out of the attic, hurricane force, Dorothy we’re not in Kansas anymore, paradigm shifting change.
BP Solar, or Massey Energy, or Akeena, Evergreen, First Solar, Sunpower, could do the same thing in West Virginia – build factories to manufacture PV Solar Modules and Solar Hot Water Panels, and hire local people to work in the factories.
It is change we can wrap our arms around, change we can celebrate. As President Obama might say, “change we can believe in. ”
—
This was planned as the Final Post in this series on the Deepwater Horizon / Macondo oil well disaster which began after Earth Day. Other posts include:
- Fossil Fuels and a Walk on the Moon,
- Drill Baby Drill or Drill Baby Oops,
- The Magnitude of the Spill,
- One Month After,
- The Chernobyl of Fossil Fuels?, and
- Magnitude, Part 2.
However, I will continue to offer my thoughts and analysis once or twice per month as the oil continues to gush forth into the Gulf of Mexico.